Turbochargers are a fascinating and intricate component that plays a vital role in enhancing an engine's power output through forced induction. In this guide, we will explore the workings of turbochargers, focusing on Rotomaster's expertly crafted turbochargers and their various components.
Introduction to Turbochargers
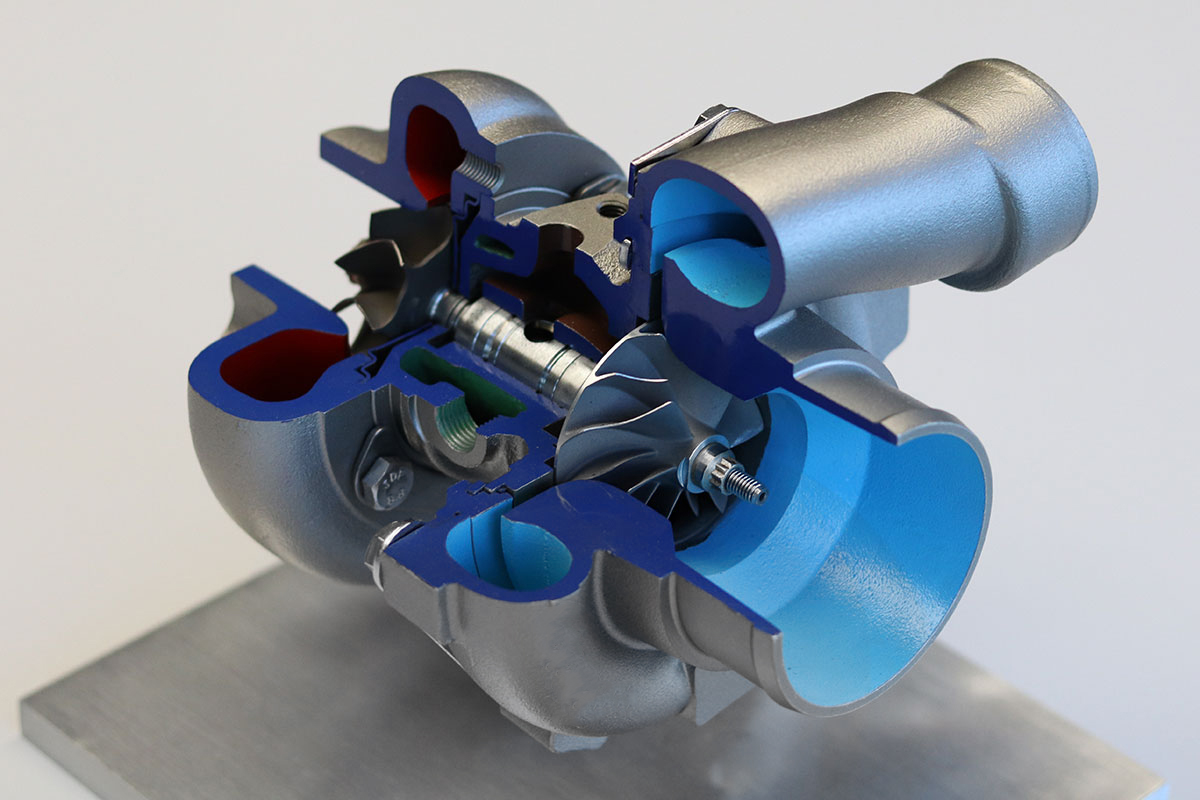
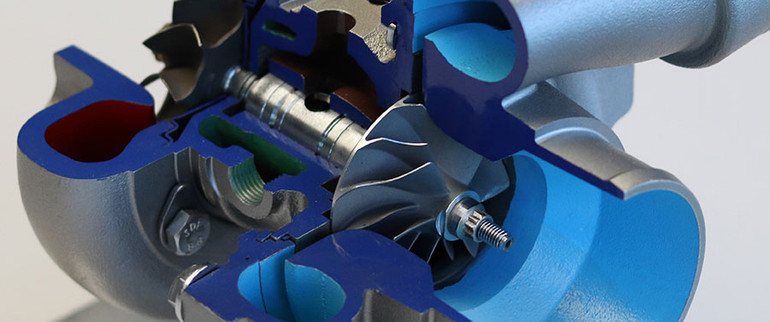
A turbocharger is a simple yet powerful exhaust-driven device designed to amplify an engine's power output. The basic principle revolves around introducing more oxygen into an engine's combustion chamber, enabling the addition of more fuel as well. This increased combustion results in higher forces than those generated by a naturally aspirated engine.
Turbocharger Operation
The turbocharger operates by utilizing hot exhaust gases directed from the exhaust manifold. These gases drive a turbine wheel situated at the core of the turbocharger. This turbine wheel is connected to a compressor wheel located on the opposite end. As the turbine wheel rotates, it propels the compressor wheel, which forces air into the engine's intake system.
Importance of Exhaust Gases and Heat
It's crucial to note that the turbocharger relies on a continuous flow of exhaust gases and heat to function effectively. These expanding gases play a pivotal role in generating the necessary airflow. Most original equipment turbocharging systems consist of a turbocharger, intercooler, and boost control components.
Components of a Turbocharger
A turbocharger is comprised of three essential sections:
-
Compressor Housing (Cold Side):
This houses the compressor wheel.The compressor wheel drives the intake air.
-
Center Section (Bearing Housing):
This central portion contains the compressor wheel, turbine shaft, turbine wheel, bearings, and passages for oil and coolant. It's responsible for the overall functionality of the turbocharger.
-
Turbine Housing (Hot Side):
Known as the hot side, this section houses the turbine wheel and often includes an integrated wastegate. The turbine wheel utilizes exhaust energy to power the turbocharger.
Intercooler's Role
As air is compressed, its temperature naturally increases. To counter this, an intercooler is used to cool the air before it enters the engine. This component can be air-to-air or water-to-air, depending on the design, and effectively improves the efficiency of the compressed air.
Controlling Boost Pressure
While increased boost pressure can enhance power output, it's important to control it effectively to prevent damage. Excessive boost can cause harm to both the turbocharger and the engine. Systems incorporate wastegates or bypass valves to regulate and manage boost pressure.
Wastegate and Bypass Valve
Wastegates control boost pressure by redirecting exhaust gases to bypass the turbine, thereby maintaining optimal flow to the turbocharger. A diaphragm-driven mechanism opens and closes the valve, ensuring proper pressure management. Bypass or pressure release valves release excess boost pressure when the throttle is closed.
Conclusion
Turbochargers are intricate systems that harness exhaust energy to deliver impressive power gains. Rotomaster specializes in crafting high-quality turbochargers, ensuring efficient and reliable performance. It's essential to consult the vehicle's service information when working with turbocharger systems to ensure proper operation and maintenance. To learn more about our range of turbocharger products, feel free to check out our Turbocharger Product Listing . We're sure you'll find something that revs your engine!